
It is well known that the emergence of the web has brought about a significant change in the concept of exchanging and acquiring information, and along with it, the methods of use and ways to retrieve data have evolved. What concerns us here are Web Applications. When comparing web applications to regular applications or what are known as Desktop Applications, web applications are slow and not as flexible or excellent as desktop applications. However, despite that, people (and we are among them) love web applications in various ways, as they enable them to access information (via a browser only) from anywhere and express their opinions and ideas through them.
Of course, this led to an increased focus on the browser market and efforts to improve it. Competition was fierce between several companies trying to dominate the browser market. Among these companies was Microsoft with its Internet Explorer browser, which it continuously developed. One of the improvements it introduced was the XMLHttpRequest object in Internet Explorer 5. The XMLHttpRequest allows JavaScript scripts on the client side to communicate with the server in the background "behind the scenes" and without the user noticing. Also, an important point is that there is no need to reload the entire page, only specific parts of the page are updated, which means creating a new layer that allows developers to make web applications more interactive and practical than before. This is because the amount of data exchanged over the network is reduced, and some processing is saved on the server side. XMLHttpRequest remained somewhat of a secret since its initial appearance, as only a few websites used it. Even those who knew about XMLHttpRequest didn't make use of it. However, Google changed that by introducing a strong set of web applications that directly utilized XMLHttpRequest, such as Google Suggest and Google Maps, prompting many others to follow suit. XMLHttpRequest was supported in most modern browsers like Mozilla, Firefox, Netscape, Opera, and Safari.
AJAX, which stands for Asynchronous JavaScript and XML, can be described as a technique or method by which web applications can be developed to be more interactive and responsive to users. Through AJAX, the need for constant server requests and full page reloads is reduced. In fact, AJAX is not a new technology or concept in web programming, but rather a name given to the use of a set of existing technologies that together form what is known as AJAX. These technologies are:
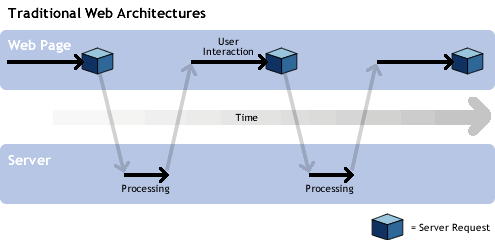
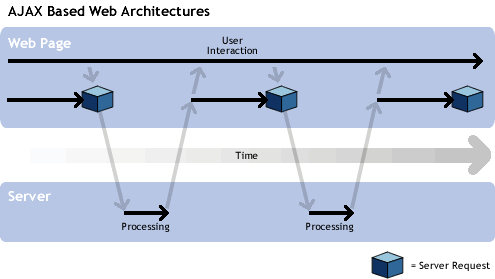
To clarify how AJAX works, let's compare traditional web applications with AJAX-based web applications.
In traditional web applications, most of the user's activities involve sending requests to the server, the server processes the requests, retrieves the data, and sends it back in HTML form to the user's browser, thereby updating the entire page. There is an important technical point in this whole "story", which is that while the server is processing the user's requests, what is the user doing during this time? Of course, waiting and staring at the mouse pointer shaped like a loading hourglass, or simply opening another browser window and browsing, for example, the Al Jazeera website. However, in AJAX-based applications, the situation is different. The requests sent to the server are only the ones that need to be updated, and this is done by the AJAX Engine, which is a JavaScript code loaded along with the page into the browser. Hence, there is no need to reload the entire page, and the user can continue working on the page while the request is being sent and the specific part of the page is updated.
The following illustrations show the user interaction processes in both traditional web applications and AJAX-based web applications.
To explain this process more clearly, let's take a real-world example: adding a new item to a List.
Let's assume we have a simple web page that contains a list displaying a group of items, and let's assume these are a list of names. Below the list, there is a text box to add a new item to the list. It is expected that when the user clicks the "Add" button, the page sends the new value to the server to be added to the database, and at the same time, updates the list displayed on the page with the new value.
In traditional web applications, the new value is sent to the server, the server processes this data (such as storing it in the database), and then the server responds by sending a new page containing the updated list with the added item. It is noticeable that in this method, resources and time are wasted because the new page returned by the server is essentially the same as the first page, with the only difference being the added item to the list. This becomes a problem in pages with large content like images and Flash, as the entire page is reloaded with a slight modification.
On the other hand, in AJAX-based web applications, they provide an answer to the following question: "How can I modify the desired part of the page without having to reload it from the server again?" This is done by AJAX applications sending the new value added by the user to the server in the background "without the user noticing, as a sub-connection to the server is established", and then modifying the desired part of the page, but this modification happens on the user side "through scripts executed by the browser to modify the page". It is noticeable that, in this way, a lot of network resources will be saved, as the amount of data exchanged is minimal (since the server no longer needs to resend the entire page to the browser), and time is saved as well, making the page more responsive to the user.
It is worth noting that dealing with this technology is somewhat complex, especially in writing the JavaScript scripts. Therefore, developers have created libraries to simplify this process, such as DWR, Sajax, and also Ajax.NET, to support AJAX on the .NET platform. Microsoft has included AJAX support in the .NET platform through what is known as Atlas.




